Overview
In this post, I am writing about one of the most important aspects
of C# which is the 4 core pillars of the Object-Oriented Programming Concept in
C#. I will explain these four pillars
and also provide further links to the related subject area.
The four pillars of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
concepts in C# provide a structured and organized approach to software
development. They are fundamental principles that help developers to create
efficient, modular, and maintainable code. By following these principles,
developers can build complex software systems that are easy to understand,
extend, and modify.
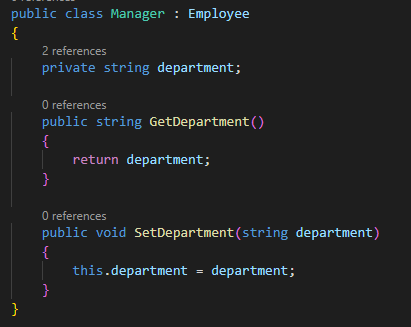
Encapsulation
Encapsulation can be achieved by defining data members as
private or protected and providing public methods to access and modify them.
This way, the data is hidden from outside interference, and you can manage the
complexity of large software systems. As
the code example below.
Click here to read further about Encapsulation
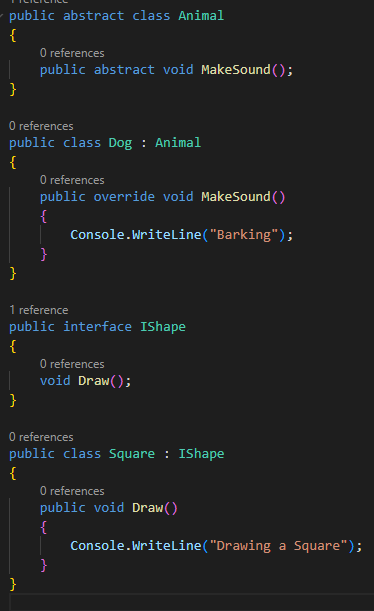
Inheritance
Inheritance can be achieved by creating a new class by
inheriting from an existing class using the colon operator. The derived class
inherits all the properties and methods of the base class, which helps in
reusing the existing code and reducing code redundancy. As the code example below.
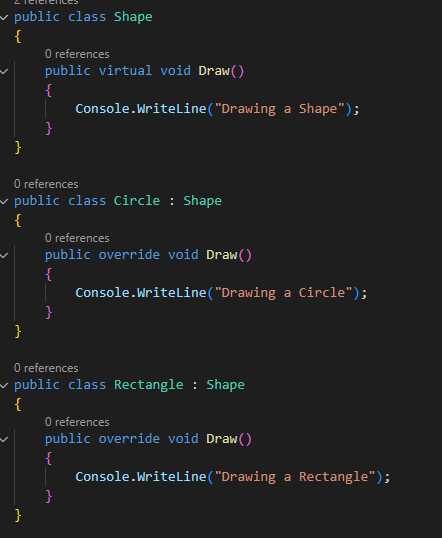
Polymorphism
Polymorphism can be achieved by creating methods with the
same name but different parameters in the base and derived classes. This way,
you can use an object of a derived class as an object of the base class, which
helps in creating flexible and extensible code as in the code example below.
Click here to read further about Polymorphism
Abstraction
Abstraction can be achieved by creating abstract classes and
interfaces. An abstract class cannot be instantiated and provides a template
for its derived classes. An interface provides a contract for implementing
classes. This way, you can represent the essential features of a class without
including the background details, which helps in reducing the complexity of the
code and provide a simplified interface to the user. As the code example below.
Summary
using the four pillars of OOP concepts in C# helps in
creating high-quality software systems that are efficient, modular, and
maintainable" is a valid and accurate statement. By following the four
pillars of OOP concepts, developers can create code that is organized, easy to
understand, and can be easily modified to adapt to changing requirements. This
results in code that is efficient, modular, and easy to maintain, which in turn
leads to the development of high-quality software systems.



Comments