Overview
In this post, I have written about my favourite concept of
Object-oriented programming, which is Polymorphism, even though I cannot say
the word Liskov Substitution Principle because
being a dyslexic person I always struggle with this word and I am no shame of
saying it openly and publicly because I do not let my weakness become a barrier
in my success and I always use my dyslexic not as my weakness but as my
strength back to the subject of this post. Polymorphism is a fundamental
concept in object-oriented programming that enables objects of different
classes to be treated interchangeably. It refers to an object's ability to take
on multiple forms or behaviours. In C#, polymorphism can be achieved through
inheritance, interfaces, and method overloading. There are two main types of
polymorphism in C#: method overloading and method overriding. Method
overloading is achieved by defining multiple methods with the same name but
different parameters, while method overriding is achieved by defining a method
in a derived class that has the same name, return type, and parameters as a
method in the base class.
Using polymorphism in C# can bring many benefits, such as
code reusability, flexibility, encapsulation, and separation of concerns. It
allows you to create classes and methods that can be used by different objects
with different behaviours, making it easier to modify or extend code in the
future. Polymorphism also helps to improve the security and reliability of your
code by hiding the implementation details of a class and exposing only the
interface. Additionally, it helps to create small, focused classes that perform
specific tasks, making your code more maintainable and scalable.
What is Polymorphism
Polymorphism is a fundamental concept in object-oriented
programming that refers to the ability of objects of different classes to be
used interchangeably, even if they have different behaviours or properties. In
other words, polymorphism allows you to write code that works with different
objects without knowing their specific types or implementations.
There are two main types of polymorphism in C#, which are
override and overloading. We have two code examples below which describe both
of these two methods:
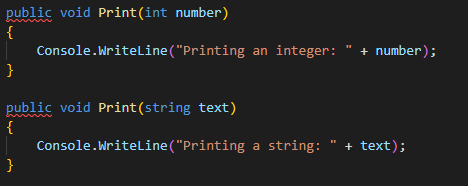
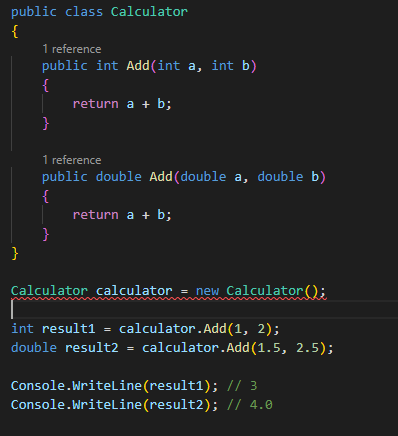
Code Example Overloading Method
Compile-Time Polymorphism: This is also known as
method overloading, which means defining multiple methods with the same name
but different parameters. When you call the method, the compiler determines
which version to use based on the number, type, and order of the parameters.
For example:
we have two methods named Print, one that takes an int
parameter and another that takes a string parameter. When we call the Print
method, the compiler determines which version to use based on the type of the
argument.
Runtime Polymorphism: This is also known as method
overriding, which means defining a method in a derived class that has the same
name, return type, and parameters as a method in the base class. When you call
the method on an instance of the derived class, the overridden method in the
derived class is called instead of the method in the base class. For example:
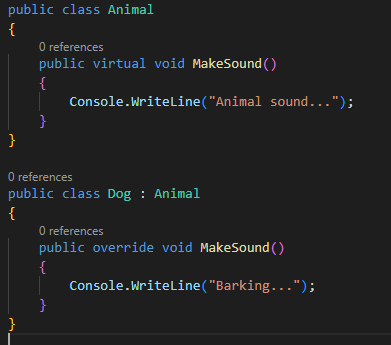
In this example, we have a Animal class with a MakeSound
method that is marked as virtual, and a Dog class that overrides the MakeSound
method with its own implementation. When we call the MakeSound method on an
instance of the Dog class, it calls the overridden method in the Dog class
instead of the method in the Animal class.
Overall, polymorphism is a powerful tool in C# that allows
you to write more flexible and reusable code by treating objects of different
types as if they were the same type.
Why use Polymorphism
Polymorphism is a fundamental concept in object-oriented
programming, and it refers to the ability of an object to take on multiple
forms or behaviours. In C#, polymorphism can be achieved through inheritance,
interfaces, and method overloading.
Here are some reasons why you might use polymorphism in C#:
- Code Reusability: Polymorphism allows you to reuse code by creating classes and methods that can be used by different objects with different behaviours.
- Flexibility: Polymorphism makes it easier to modify or extend code in the future. You can add new behaviours or override existing ones without changing the core functionality of the code.
- Encapsulation: Polymorphism allows you to hide the implementation details of a class by exposing only the interface. This improves the security and reliability of your code.
- Separation of Concerns: Polymorphism helps you separate the concerns of your code by creating small, focused classes that perform specific tasks. This improves the maintainability and scalability of your code.
Overall, polymorphism is a powerful tool that can help you
write more modular, reusable, and extensible code in C#.
How to use Polymorphism
Polymorphism in C# can be achieved through several
mechanisms. Here are three ways you can use polymorphism in C#:
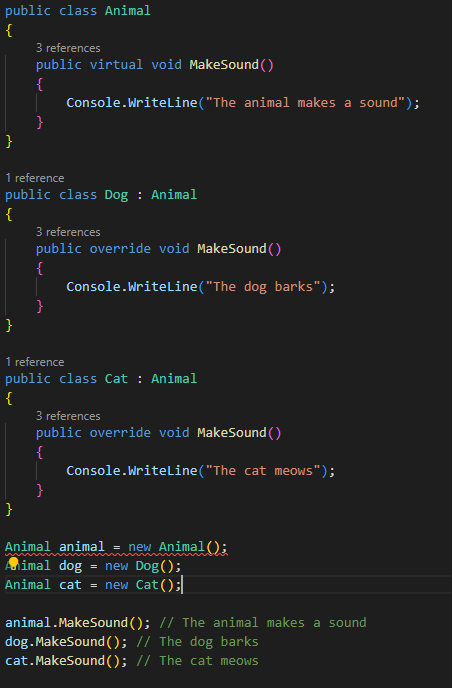
Inheritance
Inheritance allows a derived class to inherit properties and
behaviours from a base class. This allows you to create a hierarchy of classes
with increasing levels of specialization. You can then use polymorphism to
treat objects of the derived class as if they were objects of the base class.
Here's an example:
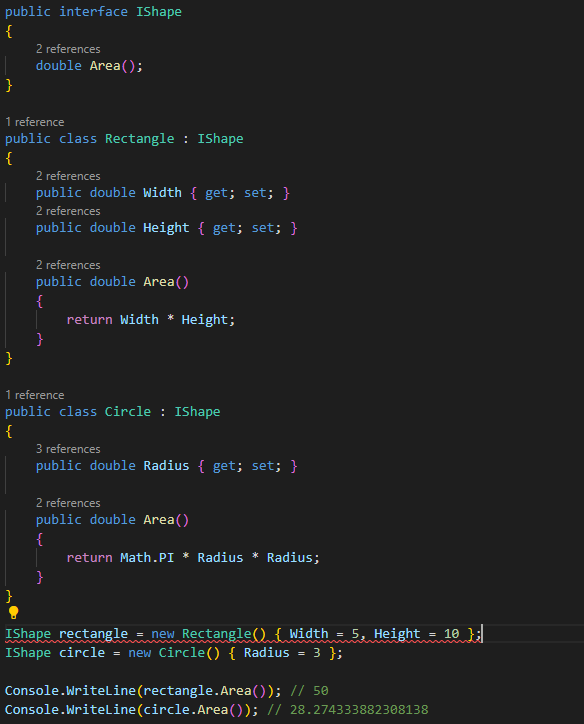
Interfaces
Interfaces define a contract that a class must implement.
This allows you to write code that is independent of the specific
implementation of a class. You can then use polymorphism to treat objects of
different classes as if they implement the same interface. Here's an example:
Method Overloading
Method overloading allows you to define multiple methods
with the same name but different parameters. You can then use polymorphism to
choose the appropriate method at runtime based on the arguments passed to the
method. Here's an example:
These are just a few examples of how you can use
polymorphism in C#. The key idea is to create classes that can behave
differently depending on the context in which they are used, and then use
polymorphism to treat these objects as if they were all of the same types.
Best Practice Using Polymorphism
Here are some best practices to follow when using
polymorphism in C#:
- Follow The Liskov Substitution Principle: This principle states that any instance of a base class should be able to be replaced by an instance of any of its derived classes without affecting the correctness of the program. This means that the derived classes should behave in a way that is consistent with the behaviour of the base class. Violating this principle can lead to unexpected behaviour and bugs in your code.( By the way I always have trouble saying this word Liskov)
- Use Abstract Classes Or Interfaces to Define Contracts: When using polymorphism, it's important to define clear contracts that specify what behaviour is expected from a class. Abstract classes and interfaces can be used to define these contracts, and then derived classes can implement the required behaviour. This makes it easier to write code that is independent of the specific implementation of a class.
- Avoid Using Sealed Classes Or Methods: Sealed classes and methods prevent further derivation or overriding. While this may be appropriate in some cases, it can limit the flexibility and extensibility of your code. Instead, consider using interfaces or abstract classes to define contracts that can be implemented by derived classes.
- Use Virtual Or Abstract Methods when Appropriate: Virtual methods allow derived classes to override the implementation of a method, while still allowing the base class to provide a default implementation. Abstract methods require derived classes to provide their own implementation. Using virtual or abstract methods can make it easier to write code that is extensible and can accommodate different behaviours.
- Use The Override Keyword To Override Methods: When overriding a virtual method, always use the override keyword to make it clear that you are overriding an existing implementation. This can help prevent bugs and make your code more readable.
- Use The New Keyword To Hide Methods Only When Necessary: The new keyword can be used to hide an inherited method with a new implementation. However, this can lead to confusion and unexpected behaviour. Use the new keyword sparingly and only when necessary.
By following these best practices, we can write code that
is more robust, extensible, and maintainable, and that takes full advantage of
the benefits of polymorphism in C#.
Summary
In Short understanding, the different types and mechanisms
of polymorphism and when to use them appropriately is essential for the effective
use of polymorphism in C#. By using polymorphism effectively, you can write
more modular, reusable, and extensible code.

Comments