Overview
In this post, I am writing about one of the C# powerful
features which is an object-oriented programming language that follows the
principles of OOPS (Object-Oriented Programming System) concepts. These
concepts are crucial in creating efficient and scalable applications. Let's look
at the key OOPS concepts in C# with code examples:
Encapsulation
Encapsulation is
the practice of hiding the internal details of an object and exposing only what
is necessary. In C#, encapsulation can be achieved by using access modifiers
(public, private, protected) to control the visibility of data members and
methods. The Internal
representation of an object is hidden from the view outside the definition of
the object. Only the required information can be accessed whereas the rest of
the data implementation is hidden.
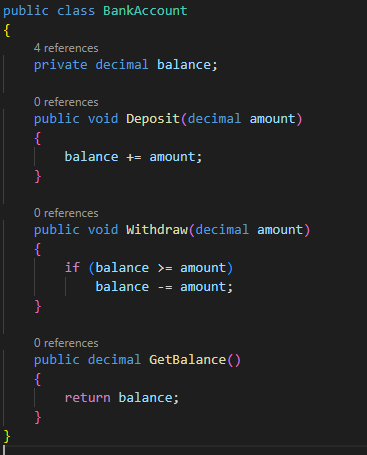
Code Example
In the example below, the balance data member is declared private, which
means it can only be accessed within the BankAccount class. The Deposit,
Withdraw, and GetBalance methods provide controlled access to the balance data
member.
Abstraction
Abstraction is the process of identifying essential
features of an object and ignoring the non-essential ones. In C#, abstraction
can be achieved by using abstract classes (classes that cannot be instantiated
but can be used as base classes) and interfaces (a collection of abstract
methods that define a contract for implementing classes). It is a process of
identifying the critical behaviors and data of an object and eliminating
irrelevant details.
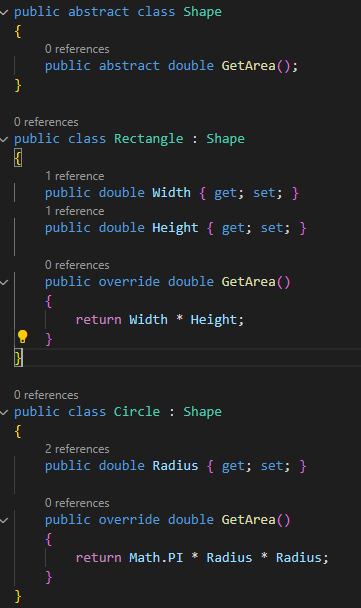
Code Example
In this example
below, the Shape class is declared as abstract, which means it cannot be
instantiated directly but can be used as a base class for other classes. The
Rectangle and Circle classes derive from Shape and implement their own GetArea
methods to calculate their respective areas.
Inheritance
Inheritance is a mechanism by which a class can
inherit properties and behaviors from another class. The class that inherits is
called a subclass or derived class, and the class that is inherited from is
called a base class or superclass. In C#, inheritance is implemented using the
colon ":" operator.
It is the ability to create new classes from another class. It is done by
accessing, modifying and extending the behaviors of objects in the parent
class.
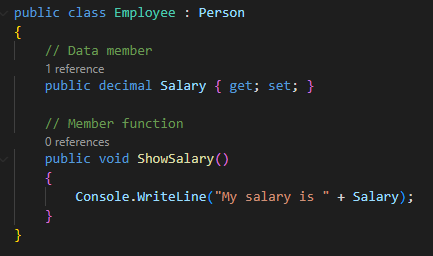
Code Example
In this example
below, the Employee class inherits from the Person class using the: operator.
The Employee class defines its own data member (Salary) and member function
(ShowSalary)
Polymorphism
The name means, one name, many forms. It is
achieved by having multiple methods with the same name but different
implementations. Polymorphism is the ability of objects to take on different
forms. In C#, polymorphism can be achieved through method overloading (defining
multiple methods with the same name but different parameters) and method
overriding (defining a method in a subclass with the same name and parameters
as a method in its superclass).
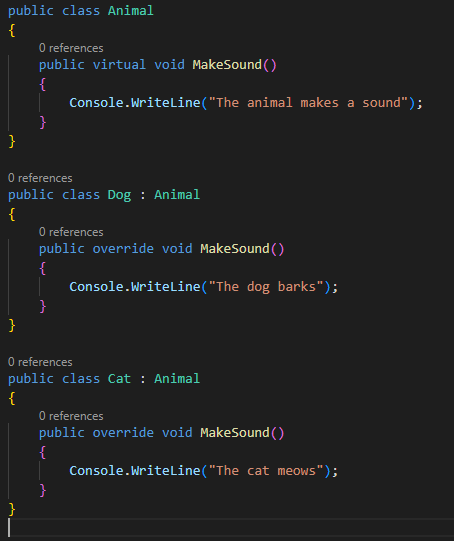
Code Example
In the example
below, the Animal class defines a virtual method (MakeSound) that can be
overridden by subclasses. The Dog and Cat classes override the MakeSound method
with their own implementations.
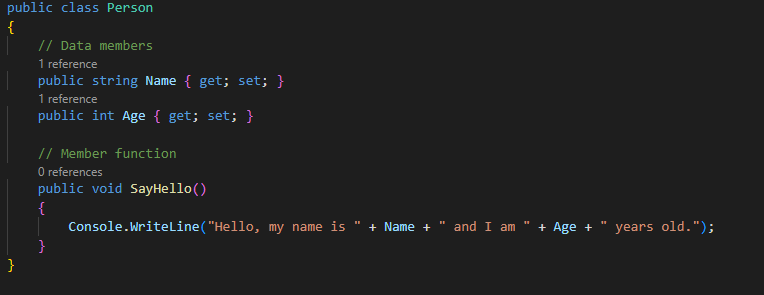
Class
A class is a blueprint or a template that defines
the properties and behaviors of an object. It contains data members (variables)
and member functions (methods) that operate on those variables.
Code Example
In the example below, the Person class defines two data
members (Name and Age) and a member function (SayHello) that operate on those
data members.
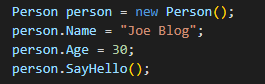
Object
An object is an instance of a class. It has its own state
(values of its variables) and behaviour (methods).
Code Example
In this example below, an object of the Person class is
created and its data members (Name and Age) are set. Then, the SayHello method
is called on the object.
These OOP concepts provide a structured and modular
approach to programming and can make code more efficient, maintainable, and
easier to understand.

Comments