Overview
This post will discuss splitting strings in C# using a built-in method named String.Split. It is used to create an array of substrings from a string based on a delimiter. You can use a string or a character as the delimiter. Split returns an array with substrings. Each substring is separated using the delimiter specified. To avoid the delimiter being misinterpreted as an escape sequence, it must be escaped using another backslash. This post will show you how to split strings using the backslash character as the delimiter. It also includes code examples.
String.Split Method
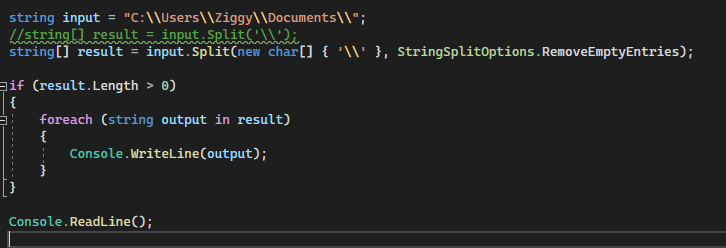
The code example below shows that a string input contains multiple backslashes. This string is called the Split method, and it uses a single backslash to delimit the input. C#'s Split method splits strings into substrings depending on the delimiter that you have specified. To use a Backslash to split two strings that have been separated by a Backslash, we must escape the backslash by using another backslash. To print each substring, we can loop through the result array.
As you can see, the string has been divided into a number of substrings. Each one is separated with a backslash.
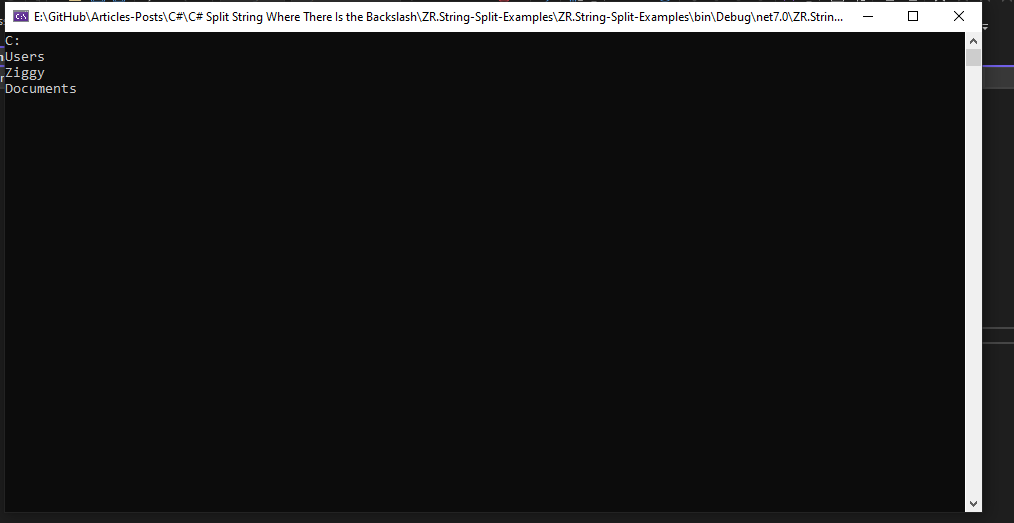
We will be able to see my computer's C: drive in the.net core console. Users, Ziggy, and documents will follow.
StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries
StringSplitOptions is an optional parameter in the Split method that can be used for removing empty substrings from any array that results from the operation. It is quite common to see empty strings in the array after splitting a string using a backslash. This is especially true if the input string ends with backslashes. In the code example below, we have passed StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries as the second argument to the Split method. This instructs the method not to remove empty substrings from the resulting array.
The code example image below shows the output of the loop we used to print substrings. The empty substring at end of the array is now gone, as you can see.
Summary
This post explains how to split strings using the backslash delimiter. The resulting array can contain empty substrings, which can be removed using the StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries option. Split is a powerful tool to split strings into substrings. It is often used in string manipulations and parsing operations. Developers can manipulate strings according to their requirements by understanding the Split method using the backslash.
I have shared the source code for this post on my GitHub Repository,
which is the following url address Ziggy Rafiq GitHub Repository



Comments