JavaScript Data Types (Primitive Data Types and Complex Data Types)
JavaScript is a dynamically typed language, which means that
variables do not have a fixed type. Instead, their type is determined at
runtime based on the value assigned to them. JavaScript has several built-in
data types that can be used to represent different types of values, including
primitive data types and complex data types.
Primitive data types in JavaScript include number,
string, boolean, null, undefined, and symbol. The number represents both integer
and floating-point numbers. The string represents textual data. Boolean
represents a logical entity and can have two values: true or false. Null
represents a deliberate non-value, and undefined represents an unintentional
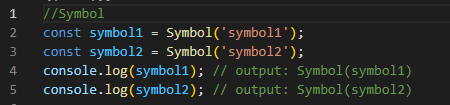
absence of any value. The symbol represents a unique identifier value.
Complex data types in JavaScript include objects and functions.
An object is a collection of properties, where each property has a name and a
value. Properties can be accessed using dot notation or bracket notation. A
function is a type of object that can be called a subroutine to perform a
specific task. Functions can be defined using the function keyword and can have
parameters and return values.
In addition to these data types, JavaScript also has several
built-in operators that can be used to perform various operations on values.
These operators include arithmetic operators, assignment operators, comparison
operators, logical operators, conditional (ternary) operators, and bitwise
operators. Understanding these data types and operators is crucial for
developing effective and efficient JavaScript code.
Primitive Data Types
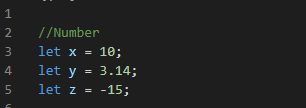
Number: represents both integer and floating-point numbers.
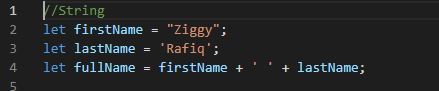
String: represents textual data.
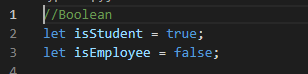
Boolean: represents a logical entity and can have two
values: true or false.
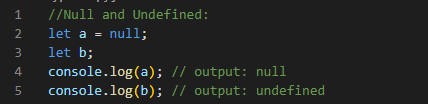
Null: represents a deliberate non-value and has a special keyword null and Undefined: represents an unintentional absence of any value and has a special keyword undefined.
Symbol: represents a unique identifier value.
Complex Data Types
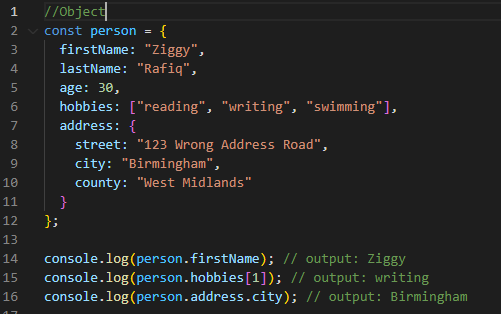
Object: represents a collection of properties, where each
property has a name and a value.
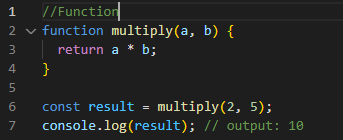
Function: a type of object that can be called a subroutine to perform a specific task.
Remember that JavaScript is a dynamically typed language, which means that the type of a variable is determined at runtime, and can change during the program's execution.

Comments