JavaScript's Conditional Statements
Overview
JavaScript's conditional statements provide the ability to
execute different blocks of code depending on whether a certain condition
evaluates to true or false. In this way, developers can create dynamic code
that reacts to changing data or user input. Here are some examples of how to
use conditional statements in JavaScript.
If Statement
The if statement is the most basic conditional statement in
JavaScript. It allows you to execute a block of code only if a certain
condition is true.
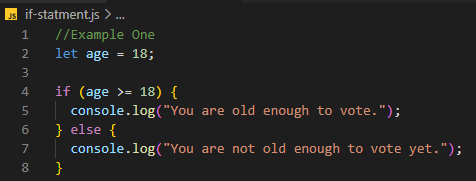
Example One
In the above example, I have given the code checks whether
the age variable is greater than or equal to 18. If it is, the first block of
code (inside the curly braces) will be executed and "You are old enough to
vote." will be logged to the console. If the condition is false, the
second block of code will be executed and "You are not old enough to vote
yet." will be logged into the console.
Example Two
In the above example, I have given a very basic if statement,
which executes the block of code only if the number is above zero.
Else-if Statement
The else-if statement allows you to add more conditions to
your code. It will only be executed if the previous condition is false.
Example One
In the above example, I have given a very basic if and else
statement, which executes the block of code if the number is above zero as positive
and as I have set the number to -3 it will execute the else statement.
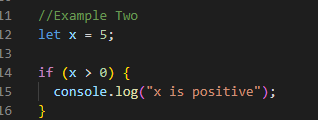
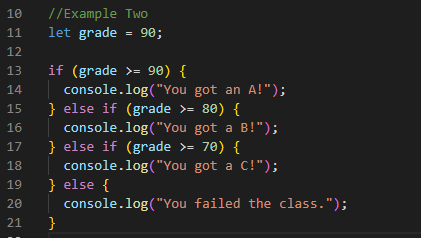
Example Two
In the above example, I have given the code that checks the
value of the grade variable and executes the corresponding block of code based
on its value. If the grade is greater than or equal to 90, "You got an
A!" will be logged into the console. If the grade is between 80 and 89,
"You got a B!" will be logged into the console. If the grade is
between 70 and 79, "You got a C!" will be logged to the console. If
none of the conditions is true, "You failed the class." will be
logged to the console.
Switch Statement
The switch statement is another way to add multiple
conditions to your code. It's useful when you have a lot of conditions to check
and you don't want to use a lot of else-if statements.
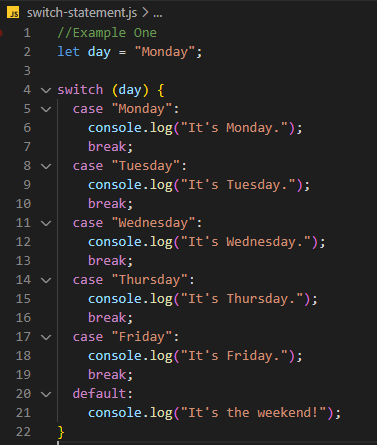
Example One
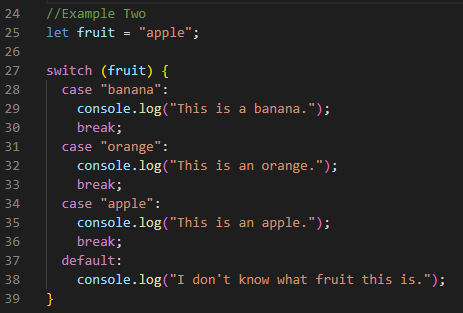
Example Two
In the above example, I have given the switch statement to check
the value of the fruit variable against three possible values. If the value is
"banana", "This is a banana." is printed. If the value is
"orange", "This is an orange." is printed. If the value is
"apple", "This is an apple." is printed. If none of these
values matches, the default block of code is executed and "I don't know
what fruit this is." is printed.
Final Thoughts
These are just a few examples of how you can use conditional
statements in JavaScript. There are many more ways to use them, depending on
your specific use case. As conditional statements in JavaScript provide a
powerful way to create flexible and reactive code. By using if and switch
statements, developers can make their code respond to changing data or user
input in dynamic and intelligent ways.


Comments